Headbangers: Rhythm Royale is the world's first competitive online music game. It pits you against 29 other players in intense musical and rhythmic battles. The challenges involved in creating this game were enormous. In this article, I'll explain some of them and show you how we managed to get around some of the limitations.
Online synchronization
The way we synchronize our 30 online players in Headbangers is unique. The game is not based on the characters' movements in space or their actions, but on their responses to musical events. We therefore decided to synchronize the client and the server to the music and its progress.
Since time and validation are managed by the server, we can detect whether a player is out of sync with the network time. Above a 100 ms time lag, the player will be resynchronized, which in practice means that the playback head will move in the music to synchronize the player at the right moment. Thanks to extensive network optimization, we were able to ensure that these resynchronizations were extremely rare.
When it came to implementing all this in Wwise, we were faced with a real challenge: Wwise is not designed for the method we wanted to apply. There's no simple way of moving the playback head of music and sounds forwards or backwards according to network time instructions.
We came up with a (largely random) trick: using the transition system to create specific rules. We noticed that by creating an immediate, fade-free transition from a song to itself in the Transitions tab of a Switch Container, we could now move the playback head as we wished.
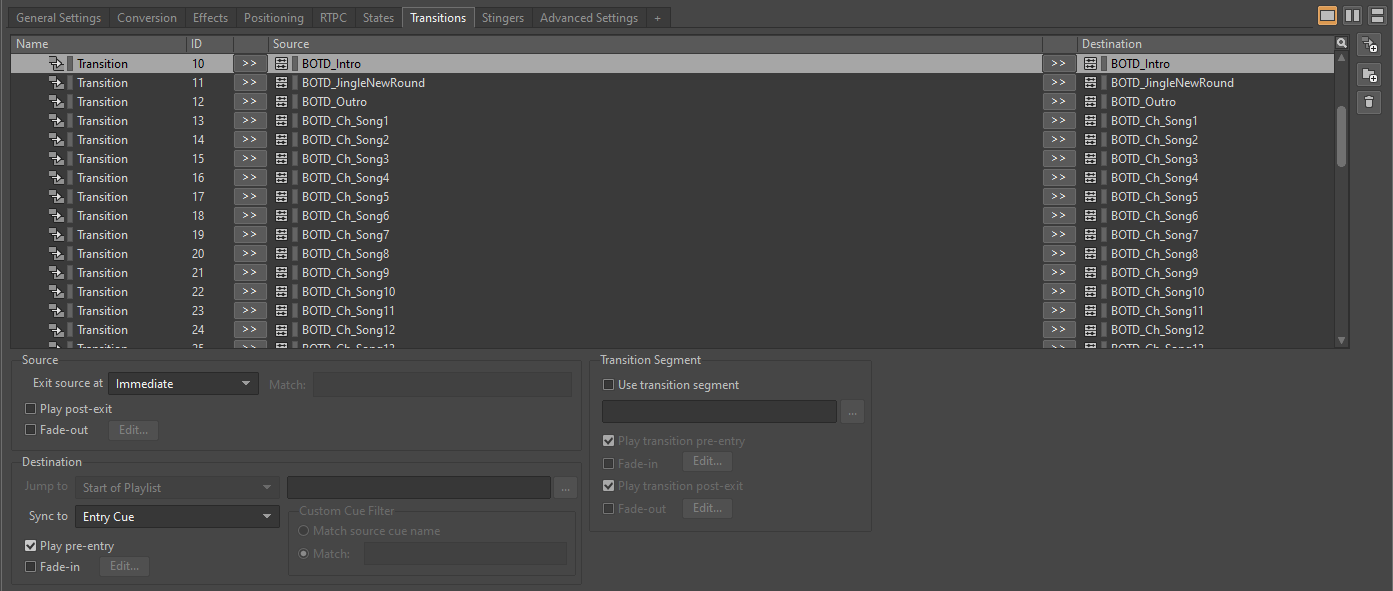
This method was quite cumbersome to apply to the whole game. Headbangers contains thousands of musical segments (over 50 hours of music), and this procedure had to be applied to every musical segment in the game. Which brings me to my next point.
SoundBank management and optimization
The sheer quantity of sounds and music contained in Wwise (tens of thousands in total) makes it certainly one of the most voluminous games in terms of sound content in the history of video games. With the game being released on all consoles and the PC, managing memory and SoundBanks (especially for the Switch) was a real challenge.
My advice is to anticipate these issues as far in advance as possible. On my end, I had to deal with this concern late in the development process, which forced me to completely rework my architecture.
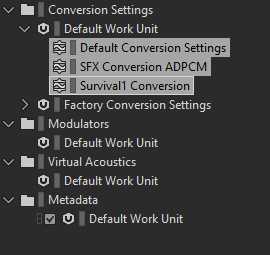
There are 23 mini-games in Headbangers. In the end, we decided to divide the game into 24 SoundBanks: one SoundBank per mini-game and one general SoundBank, containing sounds common to all mini-games, as well as menu sounds and music. The decision to distribute sounds between these SoundBanks is a key element in memory management. We therefore had to think long and hard about the use and place of each sound in the game to optimize all this.
In the same spirit of saving space and memory, we also had to optimize conversion. We therefore created several conversion parameters in Wwise, some of which are only used on certain platforms such as the Switch. So, by converting all sound effects to ADPCM on this console, we were able to save a great deal of space with very little loss of quality, while maintaining a more optimal result for music (the key element of the game) in Vorbis.
Synchronize audio feedback with player actions
Most games accept a certain latency between the moment the player presses a button and the sound feedback of the action. In Headbangers, it was impossible to be satisfied with this latency. Indeed, for a musical game, if the time lag between the button press and the sound feedback is significant, the player's entire perception is blurred.
We therefore decided to apply streaming parameters to certain sounds directly linked to gameplay. Defining that a sound will be streamed means that it can be called up more quickly, thus reducing audio latency. The key is then to set the Prefetch length for each sound, to avoid source starvation effects or untimely audio cuts.
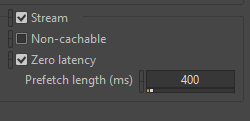
In one of our mini-games, Piano Mezzo Forte, our pigeon has to sing over background music. So we created an event for each note in each nuance (Piano, Mezzo, and Forte) and set their Prefetch length according to their characteristics and durations. Even if the end result was totally ridiculous (that’s what we wanted), this near-perfect synchronization was very important, as you can see in the video below.
Dynamic menu music
What I particularly like about Wwise is how easy it is to create dynamic music.
Even though Headbangers wasn't the game that needed most in this respect (it's a very scripted game), I had a lot of fun creating dynamic, ever-changing music in the menus, which is always appreciated by players.
Our main menu is made up of several tabs, each representing a different menu in the game: Home, Progress, Challenges, Customization, Shop, Options (see video below).
The process for creating this dynamic music effect is simple. I created one tune per menu, with the constraint that all these tunes have the same tempo, duration and harmonic progression. Then simply use Wwise transitions to create an immediate "Same time as playing segment" transition rule, and you can move from a point in one piece to that same point in another piece smoothly and efficiently.
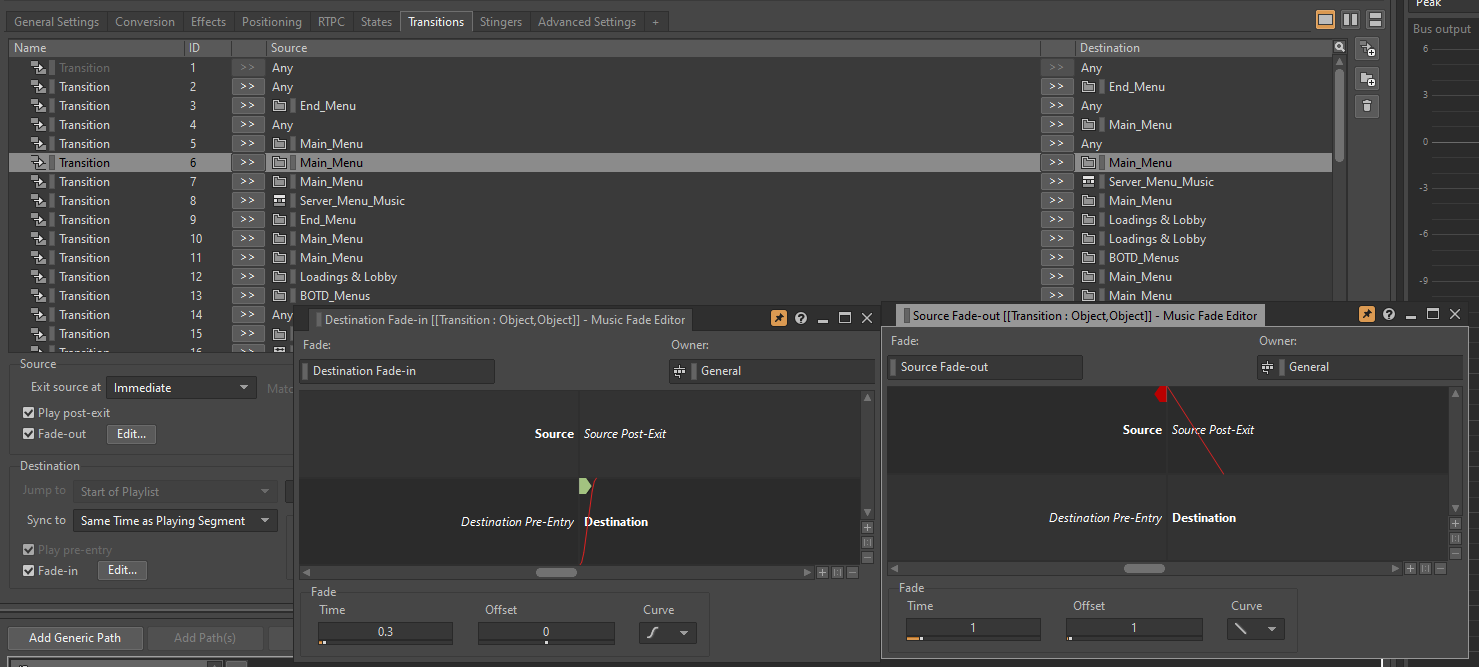
It's all very simple and quick to set up, and the effect is always satisfying. Wwise really helped us meet a lot of the challenges on Headbangers, and we consider it to be a really reliable and robust audio engine, yet accessible and intelligent enough for composers or sound designers.


评论