I’m Levi Bond, I produce audio for games under the moniker ‘dBXY Collective’ with a couple of colleagues, and together we worked with developers ‘High Tea Frog’ on their recent tranquil release, Seashell. Below is a brief overview on how we approached our most dynamic project to date, and utilised the tools available in Wwise to enhance the player experience.
The first thought we came to during ideation was that we wanted this game to not actually have any kind of fixed soundtrack – that is to say there would be no predictable, looping audio element playing throughout. This is a relatively uncommon approach and it was the first time I’d considered producing audio for a game in such an overtly dynamic way. We wanted the player to be influencing all the audio in the game, almost like they were ‘playing’ the soundtrack simply by interacting with the game. This was an ethos that stuck with us, however the development team raised an interesting point; that they would like the player to be able to have the game sitting idly in the background, and still hear a relaxing soundscape happening automatically (almost like something you could fall asleep to, without having to interact). Clearly, this meant that we had to revisit our ‘Interaction = Audio’ approach, but we were still determined to stick to the idea of having the audio be inconstant.
So now we realised that we needed a few different audio elements:
- Something musical that plays regardless of player interaction (developer request outlined above)
- Something musical that plays upon player interaction (to add dynamics, our original idea)
- Something that resembles diegetic sound, as opposed to music (for padding mainly)
These objectives ultimately became the following actual elements in-game:
- Randomised pad chords
- UI sounds, resembling a melody upon interaction
- Diegetic ambience (waves)
I’ll briefly break down each of these elements before wrapping up, beginning with the randomised pad chords.
In line with the developers’ request for some relaxing music that continues playing without any interaction, we produced about 6 different chords in the key of Eb. These chords play in a slow-attack, long-release pad synth timbre (I think it was a combination of a NI Massive sound, and one of Logic Pro’s built-in ES2 synths). We also repurposed the chords with inversions to provide more variety, and more importantly we completely altered the timbre for when the player was in the Journal view as opposed to the Beach view – The Beach featured a brighter chord sound, whereas the Journal chords were less present, with a gentle low-pass filter. Logistically, this was a case of exporting each individual chord sound to its own audio file, then putting these files into a Random Container in Wwise, with the Play Mode set to Continuous, with the Loop set to infinite, and a Trigger rate of around 6.5 seconds in the Transitions option. This results in the game playing a slow, freeform piece where the same chord sequence is essentially never heard twice. I also exported 3 different lengths of silence and placed them in the same Random Container, adjusting the likelihoods appropriately, so the gaps between the chords was constantly changing too. This entire process was repeated again for the softer Journal chords, leaving me with 2 Random Containers that played their own unique sequences when triggered. It took some careful manoeuvring to have the transition between both containers sound natural in the game (paying attention to the fades on the Stop events), but I was happy with the outcome.
For any music theorists reading, the chords we wrote for the Random Containers are all in the key of Eb - EbMaj, BbMaj6, Gm7, Fm7/Eb, Cm7(sus4), and AbMaj7. These chords are all relatively ambiguous, none suggesting strong complete resolutions, or any overly emotive major or minor chords (1st, major/minor 3rd, 5th). The ambiguity means these chords can drop in and out periodically in any order without sounding like they have a beginning or end, seamlessly looping throughout, without sounding distracting.
Next up is the melodic UI elements – the audio elements which only trigger when interacted with.
Almost all of the UI audio in Seashell triggers a pitched note (or collection of notes). Obviously when writing these sounds we had to bear in mind all the aforementioned chords that could be playing in the background, to make sure there’s no tonal clashes that could occur between the chords and the UI. There are some aspects which have a more percussive and less tonal sound, to avoid monotony on sounds which are heard very frequently (for example, hovering over a new menu selection). But other than those rare cases, pretty much all the UI audio is pitched so that player gets this feeling of writing a melody over the randomised chords playing underneath.
It would probably be tedious for me to go into detail on all of the UI sounds throughout the entire game, but I will talk a little about our decisions behind the ‘Shellodies’. Each shell in the game actually has its own unique melody, we referred to these as ‘Shellodies’. The shellodies play when picking up a shell on the Beach, or clicking to read more about a shell in the Journal. The idea was that players could begin to recognise a shell not just visually but also by simply hearing the few notes that sound when picking it up. Furthermore, the number of notes in each shellody actually indicates the rarity of the shell to the player, with a common shell only having a 2-note melody, an uncommon shell having a 3-note melody, and so on. There’s a hot tip for the rare-shell hunters!
Similarly to the randomised synth pad chords, we created 2 instances of every single shellody, the first with a brighter xylophone-esque timbre for the Beach view, and the second with a soft felted piano timbre, for when selecting the corresponding shell in the Journal view (obviously the actual notes were still the same per shell, to enforce this idea of recognising a shell by the melody alone). The video below demonstrates a couple of the shellodies in the game, as well as the change in timbre between the Beach and Journal view.
Finally, the diegetic ambience - the sound of lapping waves.
This element is a relatively simple but equally important layer of the soundscape. The waves are one of very few diegetic sounds heard in the game (‘diegetic’ means a sound that would actually occur within the context of the virtual environment, if it was real). Connoisseurs of the serene will know that waves are traditionally used to emphasise rest and soothing, in places of calm such as spas, or massage parlours. So this sound is a perfect fit for a game all about tranquility, to the extent that I probably would’ve used a waves sound even if the game didn’t take place directly on a beach!
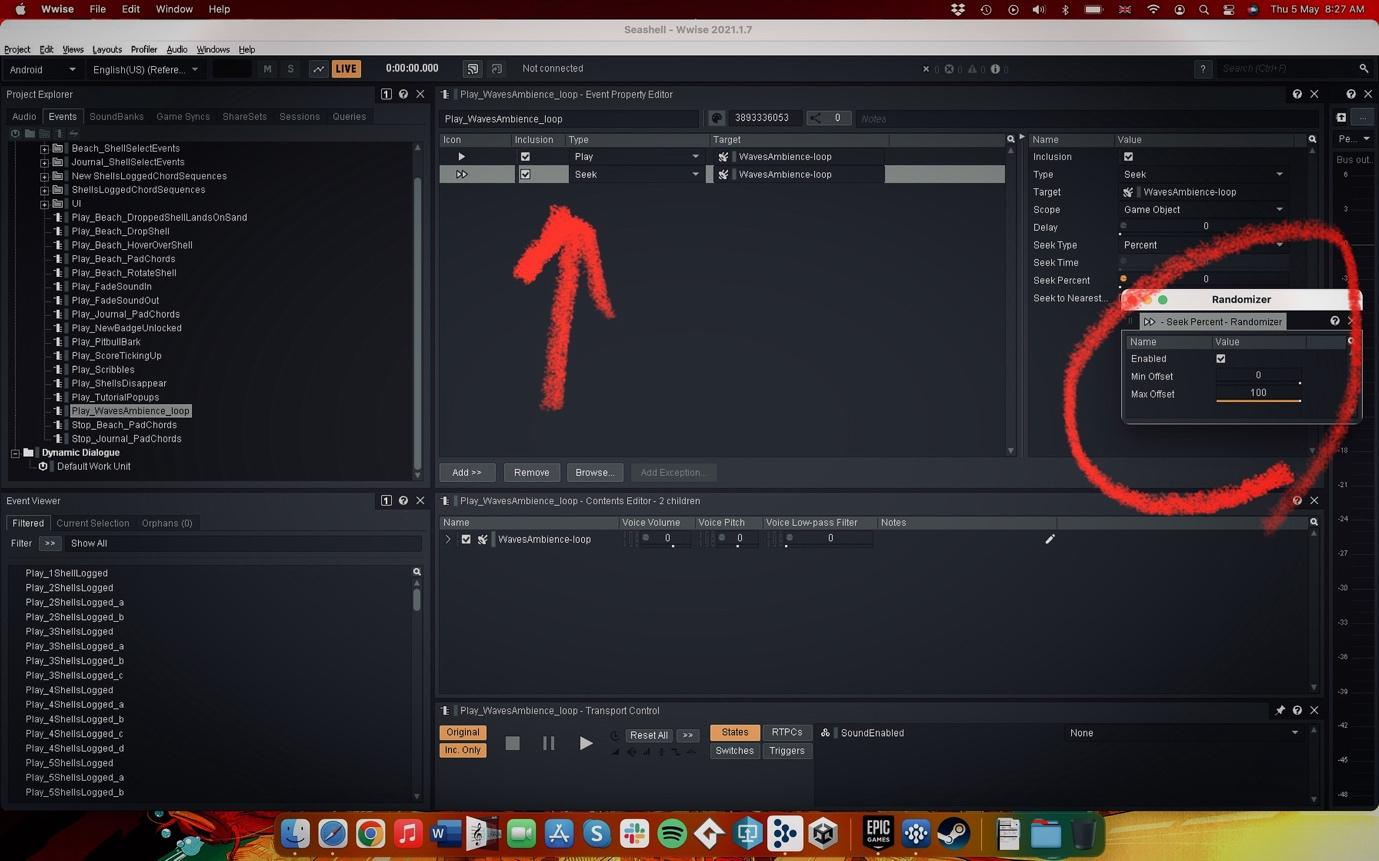
One thing to be careful of with looping background layers like this is that the player doesn’t recognise that the sound is a loop. If they start to realise where the beginning/end of the sound is then the immersion is compromised. To combat this I utilised the Blend Container in Wwise to not only have multiple layers of waves playing over each other (with different looping lengths), but I also added a Seek action on the Play event for the Blend Container and fully randomised the Seek value (0-100). This results in a seamlessly looping waves sound which never really sounds the same twice, and never begins at the same point upon starting the game up.
To summarise, High Tea Frog did an amazing job making a reposeful, calming game, and I was inspired by their commitment to deliver a sincere experience. I believe I delivered an equally considered ingredient to complement their work, and I genuinely could not have done so without the tools made available to me in Wwise. Try out the game if you haven’t already and thanks for reading.


댓글